The study filled a gap in data on freshwater biodiversity. The studied species were selected because their diverse positions within food webs present a holistic view of the health of freshwater ecosystems globally.
The species inhabit inland wetlands such as lakes, rivers, swamps, marshes and peatlands — areas the researchers said have been reduced by more than a third since 1970. Other research has documented the status of mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians that share these freshwater ecosystems and often face their own unique threats.
Severe threats
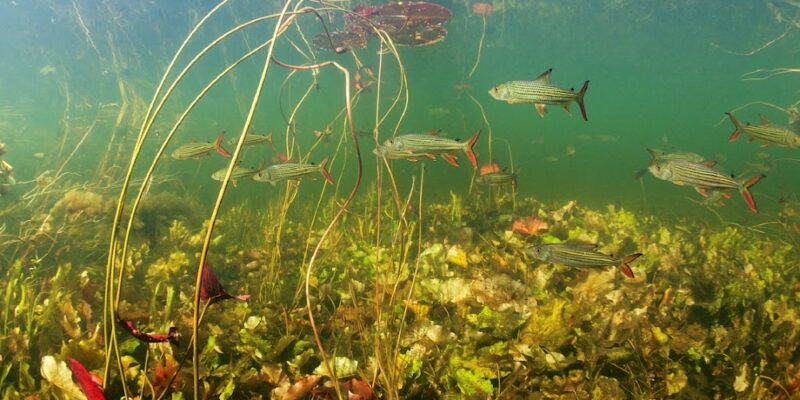
Of the animal groups investigated in the new study, the highest threat levels were documented in the crustaceans (30% threatened) followed by the fish (26%) and the dragonflies and damselflies (16%).
“Freshwater ecosystems are ecologically important because of the diversity of species they support. Some of them may have high numbers of species that are restricted just to those systems — a single lake or pool or river,” said Northern Arizona University freshwater conservationist Ian Harrison, a member of the IUCN species survival commission and a co-author of the study.
“They are also important in terms of the ecosystem services they supply: carbon sequestration in terms of peat bogs; food in terms of fisheries; medicines from plants; as well as cultural and aesthetic values. Freshwater reeds are used for building houses in some areas. Freshwater ecosystems contribute $50-trillion in value annually by their provision of natural processes supporting human wellbeing,” Harrison said.
The researchers identified four places globally with the largest number of threatened freshwater species: Lake Victoria in Africa, Lake Titicaca in South America and regions in western India and Sri Lanka.
Lake Victoria, the world’s second-largest freshwater lake by surface area, is bordered by Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda. The key threats identified to species were pollution, overfishing, agriculture and invasive species, particularly the Nile perch and water hyacinth. Lake Titicaca is situated on the border between Peru and Bolivia in the Andes. It was found to face a similar group of threats as Lake Victoria. Both lakes boast a rich diversity of fish.
“There is an urgent need to focus on freshwater conservation to halt the decline in species, and this can be achieved through a more integrated management of water resources that can include the maintenance of ecosystem functions within the process of addressing the obviously important human needs for water,” Harrison said.
“The particular value of this study is that it shows us which river basins, lakes et cetera, are the ones where the conservation challenges are most urgent and serious,” Harrison added. “And we can compare this to what we know about existing protections, and identify where there are gaps and where there are conservation needs. And it acts as a baseline of information from which we can track progress, to see if our actions are reducing threats.”
Reuters










Comments